Electrolyte additives for high-voltage batteries
Lithium-ion batteries are widely used as electrochemical storage devices and can be applied for a wide range of applications. In order to significantly raise battery performance, especially in electromobility and stationary energy storage, solutions for improving the energy and power density of storage cells are researched.
State of the art
One approach to increase performance is to use high-voltage cathode materials such as lithium cobalt phosphate or lithium nickel manganese oxide, which allow a significant increase in cell voltage. In the case of the application of higher voltages of 4.5 V and more, however, organic liquid electrolytes used up so far show only limited chemical stability, which leads to a continuous degradation of the electrolyte, to rising internal resistance and finally to the battery cell drying out. Thus, repeated charging quickly results in a performance decrease of the battery.
Technology
At the Helmholtz Institute Ulm (HIU) of KIT, scientists with a special electrolyte composition have succeeded in ensuring the necessary stability and at the same time increasing the efficiency of high-voltage batteries. In addition to the usual components of a liquid electrolyte, such as organic solvent and conductive lithium salt, the electrolyte is specifically enriched with two complementary additives: phosphite and carbonate. The addition of electrolyte additives improves the ionic conductor properties and stabilizes the cathode-electrolyte interface, thus preventing electrolyte degradation at the cathode surface.
Advantages
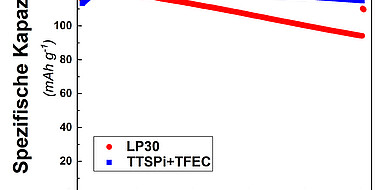
Only the synergetic combination of the two additives results in a significantly increased capacity with enhanced cycle stability, energy and power density. Lithium-ion batteries are thus suitable for use in the high-voltage range > 4.5 V. The invention reduces charge losses during charging and discharging.
Options for companies
The electrolyte additives have already been tested on a laboratory scale and could be used commercially in cell production without significant changes in process engineering. KIT is looking for partners for development projects or to license the electrolyte composition for high-voltage batteries.
Your contact person for this offer

Innovation Manager Energy Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT)
Innovation and Relations Management (IRM) Phone:
Email: transfer@irm.kit.edu