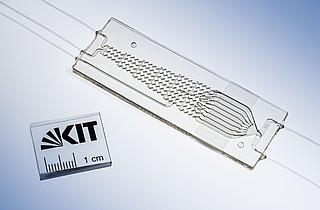
Freely programmable lab-on-a-chip
Microfluidic chips, known as lab-on-a-chip, are used to automate analytical processes in medicine, pharmacy and chemistry. Often, the chips are customized, which results in high manufacturing costs. Programmable chips, on the other hand, fulfill the requirements for flexible use and lower-cost production in large quantities.
State of the art
The transport of fluids or droplets by electric fields is already possible in digital microfluidics by means of electrowetting, electrophoresis and electroosmosis. (Bio-)chemical samples that are dissolved in carrier fluids are thus mixed, caused to react and the results are analyzed. However, the widespread use of these methods on small length scales fails due to high voltages, excessive heat generation and low efficiency.
Technology
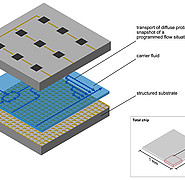
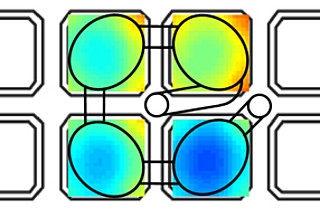
With a new method for generating liquid flows, scientists from the Institute for Thermal Energy Technology and Safety (ITES) at KIT overcome these disadvantages. Here, the drive is provided by traveling wave electroosmosis (TWEO). A chip made of semiconductor material is separated into tiny pixels in a matrix-like array. Electrodes are embedded in each pixel, which generate an electric field and specify a flow direction and velocity. Thus, one or more material flows of the samples can be moved along any path in a freely programmable electric field on the given pixel array. Due to the small dimensions of the individual pixels, only low voltages are required for this. The modular structure allows efficient control of the individual pixels in the grid. The scientists obtain an increased flow velocity by optimizing the geometry adapted to load concentration and double layer.
Advantages
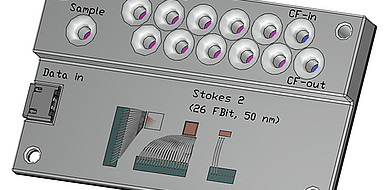
The overall concept for the chip (STOKES2) with integrated control is superior to customer-specific systems in its flexibility due to the programmability. The low-voltage electroosmotic drive unit with alternating current in a compact 3-electrode design generates high flow velocities with comparatively low heat generation so that sensitive samples can be manipulated. The developed electrode array can also be economically manufactured using lithographic methods.
Options for companies
The STOKES2 platform technology is particularly interesting for diagnostic test systems. KIT is looking for partners for the realization of chip-integrated measurement techniques and applications.
Your contact person for this offer

Innovation Manager Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT)
Innovation and Relations Management (IRM) Phone: +49 721 608-25587
Email: rainer.koerber@kit.edu